Information on Sofnolime® CO2 Absorbent for Rebreathers
© Copyright 2007-2024 by DiveGearExpress.com, portions are © Molecular Products

Sofnolime® is the Molecular Products brand name for its soda lime formulations of carbon dioxide absorbent, optimized for the removal of carbon dioxide from recirculated breathing gas systems. Sofnolime is a carefully prepared, low dust, mixture of calcium hydroxide (~75%) and sodium hydroxide (3%) with a precise amount of water moisture and binding agents.
Characteristics of Sofnolime
Soda lime type carbon dioxide absorbents are composed of off-white color hard granular particles with no significant odor, available in several grades. The main differences between the grades are particle size, shape, moisture content, hardness and testing regime. The various grades also have differing carbon dioxide absorption characteristics under various environmental conditions.
Absorbent is produced in a range of particle sizes. Size has an effect on the speed of reaction, which in turn affects the volume of the reaction zone and the duration of the absorbent bed. The smaller the particle size, the faster the reaction and the smaller the reaction zone volume and the more efficient the carbon dioxide absorption. There is also some evidence that smaller particle sizes perform better than larger sizes in very cold temperatures. However, the smaller the particle size, the greater the pressure-drop across the absorbent bed which in some applications is a critical consideration.
Sofnolime particles have either a semicircular shaped cross-section for the larger size particles or a triangular shaped cross-section for the smaller size particles. These unique particles have a higher surface to volume ratio than ordinary spherical particles. The irregular shapes provide maximum carbon dioxide penetration into the particles, by minimizing the distance to the center of the particle, thereby increasing the absorption capacity. The irregular shapes also produce a long winding path for the gas through the bed without creating any large straight channels, which results in very good gas to solid contact.
Carbon dioxide absorbents based on soda lime require specific amounts of moisture to be present to work efficiently. The amount of water incorporated into the different grades of material has been optimized for specific applications. Absorbent will not work if the water present in the material is frozen or the material has been allowed to dry out.
Sofnolime is formulated to have excellent hardness characteristics. The hardness of the Sofnolime granules minimizes breakdown and the formation of dust during handling. Compared with other soda lime products, Sofnolime has very low dust levels, and excellent attrition resistance. In addition to reducing nuisance issues, minimizing dust can also help minimize the pressure-drop across the absorbent bed. In rebreather applications, the reduced dust means reduced risks from caustic cocktail.
Some absorbents can optionally be formulated to contain dyes that temporarily change color to visually indicate absorption activity. Molecular Products states the dyes used in the indicating versions of Sofnolime do not have any adverse effects and do not affect performance. However, Navy specifications for absorbent in diving grades specifically prohibit the use of indicator dyes, therefore Dive Gear Express only stocks the NON-indicating formulation.
Chemistry of CO2 Absorption
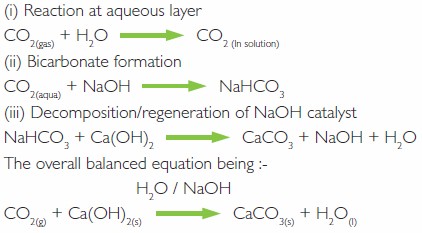 The carbon dioxide [CO2] is removed by a water mediated base catalyzed exothermic chemical reaction, converting the calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and CO2 to calcium carbonate [CaCO3] and more water.
The carbon dioxide [CO2] is removed by a water mediated base catalyzed exothermic chemical reaction, converting the calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2] and CO2 to calcium carbonate [CaCO3] and more water.
The reaction proceeds in 3 stages as described in the equations. The base, in this case sodium hydroxide [NaOH], is not used up but acts as a catalyst.
Mechanics of CO2 Absorption
A bed of absorbent is contained in a scrubber housing. The gas to be filtered is passed through the absorbent bed. The diagram illustrates the mechanics of carbon dioxide absorption in the absorbent bed of the scrubber, plotting time against the level of carbon dioxide in the gas stream at the outlet of the scrubber.
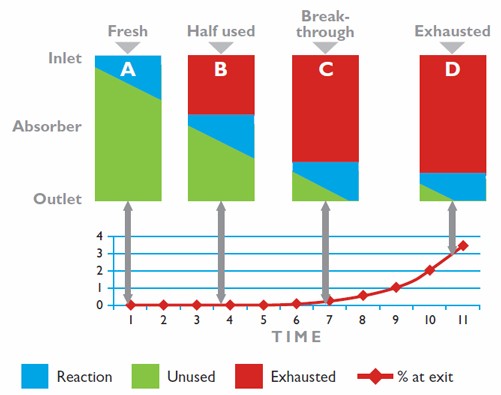
(A)- Initially the absorbent is fresh and the reaction is established where the gas enters the absorbent bed. The gas at the outlet contains no carbon dioxide.
(B) - As the reaction continues, the diagram shows the reaction zone on a diagonal to illustrate the reaction area is always uneven as it moves through the absorbent bed.
(C) - As the leading edges of the reaction zone reach the end of the absorbent bed, breakthrough occurs and the level of carbon dioxide in the gas exiting the scrubber begins to increase.
(D) - As the core of the reaction zone reaches the end of the absorbent bed, the carbon dioxide levels will very quickly increase because most of the absorbent is exhausted. Shortly thereafter, the reaction ceases as no more carbon dioxide can be absorbed.
The scrubber will have a finite life based on the quantity of Sofnolime it contains and the level of CO2 within the filtered gas. The scrubber will remove all of the CO2 (assuming it is appropriately sized for the application) until the Sofnolime is consumed, at which point the CO2 level in the exiting gas stream begins to increase - this is termed breakthrough.
Applications for Sofnolime
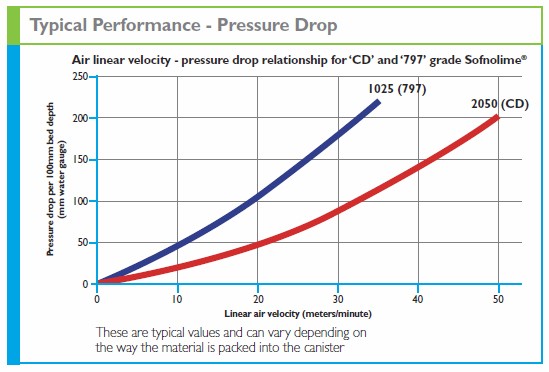
Diving environments have temperature ranges and elevated pressures (resulting in higher gas densities) that are particularly demanding for carbon dioxide removal. The Sofnolime diving grades are formulated for use in closed-circuit or semi-closed rebreather systems as well as saturation diving systems. Sofnolime 2050 CD-Grade is a 2.0mm to 5.0mm (4-8 British Standard Mesh) particle with a semicircular shaped cross-section. Sofnolime 1025 797-Grade is a smaller 1.0mm to 2.5mm (8-12 British Standard Mesh) particle and has a triangular cross-section which combines to give a higher carbon dioxide absorption capacity compared with CD-Grade. Both grades have 16%-20% moisture content, and the CD-Grade is slightly harder than 797-Grade. Diving grade products are manufactured in both non-indicating and white-to-violet indicating versions. The typical usable absorption capacity of 797-Grade is 150 liters/kg and CD-Grade can typically absorb 110 liters/kg of carbon dioxide, or about 25% less than 797-Grade. CD-Grade is generally used in less demanding applications or in equipment requiring a lower pressure drop across the absorbent bed. In October 2012, Molecular Products published a Technical Report: Performance Testing of Sofnolime 797 and Other Diving Grade Soda Lime Samples at Depth under realistic diving conditions that demonstrated it's superiority over the competition.
The Sofnolime military grades are for use in submarines and combat rebreather systems and are tested to certify they meet or exceed NATO STANAG 1411 specifications. Sofnolime 1025 D-Grade significantly exceeds STANG 1411 Grade "A" specifications and Sofnolime 2050 L-Grade meets STANAG 1411 Grade "B" specifications. In applications where NATO STANAG 1411 certification is not required, commercial sector products could be substituted. Sofnolime 1025 797-Grade non-indicating could be substituted for Sofnolime 1025 D-Grade, and Sofnolime 2050 CD-Grade non-indicating could be substituted for Sofnolime 2050 L-Grade.
The Sofnolime medical grades are used in low flow, minimal flow and closed circuit inhalation anesthesia systems where the pressure-drop across the absorbent bed must be negligible. Medical grade has very different reaction characteristics than diving grades, and medical grade carbon dioxide absorbents should not be used in diving applications. For more information cautioning against the use of medical grades in diving applications, see this Advisory Letter from Molecular Products.
Transport of Sofnolime
Sofnolime is classified under international and US Department of Transportation (DOT) rules as non-hazardous for transport by road, rail, sea and air. Sofnolime is classified only as a irritant under European supply legislation. There is no US equivalent classification and in the US the DOT does not require any special labels or placards for transport. Occasionally, transport personnel will incorrectly assume Sofnolime is a Hazardous Material (HazMat) and either refuse it or levy special HazMat surcharges. In these cases it might help to have a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (English) at hand. Point out section #14 of the SDS that documents Sofnolime has no transport restrictions or UN Number. You might produce a copy of the Official Statement Letter from Molecular Products declaring Sofnolime is classified as non-hazardous material for transport.
Storage of Sofnolime
When correctly stored, intact and unopened plastic containers of Sofnolime will maintain absorption capacity for five years. Sofnolime does not require any maintenance during storage but should be stored in a temperature range of 32 - 95°F (0 - 35°C). Storage at high temperatures or exposure to the heat of direct strong sunlight can result in reduced efficiency and service life due to moisture loss or uneven distribution of moisture. Containers must not be stored where they can become subject to the following: Direct strong sunlight; contact with or close to incompatible chemicals or acids; partial or total water immersion; atmospheres with abnormal concentrations of carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide or other acidic gases; freezing conditions; excessive stacking loads (two pallets is the maximum stacking height.)
Handling of Sofnolime
It is critical to follow the specific absorbent handling and use recommendations of the equipment manufacturer for your specific model scrubber. Use of the improper product can cause problems such as excessive work of breathing or shortened scrubber times. Watch this fifteen minute video showing underwater footage of a genuine real-life rebreather emergency as a result of improper handling of carbon dioxide absorbent.
Being mildly alkaline, absorbent should not be allowed to come into prolonged contact with sensitive skin. All contact with the eyes or mucous membranes must be avoided. During filling and emptying of absorbers wear suitable eye/face/hand protection and nuisance dust masks should be worn when working with absorbent granules. See the Sofnolime Safety Data Sheet (Multiple Languages) for detailed handling recommendations and first aid procedures.
The manner in which absorbent is loaded into the scrubber to create the absorbent bed is critical to the performance of the product. The equipment manufacturer instructions for loading and operating the equipment must be followed precisely in order to achieve the expected Sofnolime performance. Partially expended absorbent beds must never be disturbed and subsequently reused, as the performance of the absorbent bed will be significantly impaired by the mixing of used and unused material.
If absorbent containing usage indicator dye is used and then left to stand, the dye will slowly change back to the original color. This reversal of usage indication is due to small quantities of unreacted sodium hydroxide in the interior of the granules slowly migrating to the surface of the granules. Absorbent in this apparently regenerated condition, must never be reused as the absorbent capacity will very quickly become exhausted. If relying on the dye to indicate usage, always empty or change the absorbent bed immediately after use to avoid inadvertent reuse.
Disposal of Sofnolime
Sofnolime kegs are constructed from high density polypropylene (HDPE) which can be recycled when emptied and cleaned. In the US, absorbent granules can normally be disposed of as ordinary trash in land fill, although local legislation may apply to disposal or recycling. In marine environments, Dive Gear Express does not advocate the practice of dumping expended diving grade material overboard, instead it should properly handled as shipboard trash. US Federal law prohibits the overboard disposal of plastics and other shipboard trash.
The major component of expended absorbent is calcium carbonate, which is environmentally benign because it is a naturally occurring mineral. Depending on local regulations the material may be classified as hazardous waste due to the very small amount of sodium hydroxide present and the irritant nature of unexpended calcium hydroxide. A proportion of the sodium hydroxide will be water leachable. Other contaminants may be present in used Sofnolime depending on the materials it is exposed to during use.